The Evolution of Mating Systems Is Most Likely Affected by
B care required by young. Theory why might different mating systems affect the.
Changes in mating systems because of environmental change can consequently alter the demography and genetic-make up of populations.

. Population size care required by young and certainty of paternity. Care required by young and certainty of paternity. A quantitative approach to mating system analysis emphasizes the measurement of sex differences in the variance in relative fitness as well as genetic correlations that may arise among breeding pairs.
571582 find that the presence or absence of dichogamy is diagnostic of selfing and outcrossing syndromes. Care required by young. The evolution of mating system is most likely affected by Sexual dismorphism Mating system in which females are more ornamented that males Polyandry What fitness benefit of polygamy in birds that rear young that are precocious develop and mature rapidly.
School University of Toronto. Theory Why might different mating systems affect the evolution of a diversity. They have been evolved through the complexity of the need to fertilize the eggs.
Outcrossing organisms put together new combinations of genes. Part A The evolution of mating systems most likely affected by population size_ care required. Care required by young and certainty of paternity.
The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by A population density The evolution of mating systems is most likely School Jefferson State Community College. This can have serious consequences for the viability and persistence of populations and ultimately for. So Oh imagine we have a nasty here and the bird nest and it has four eggs in it.
On this basis you can probably conclude that the species is polygamous The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by sexual dimorphism The mating system in which females are more ornamented than males is polyandry What is the fitness benefit of polygamy in birds that rear young that are precocious develop and mature rapidly. Part A The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by population size. A certainty of paternity b population size c care required by.
Mating systems have been evolved throughout the years to increase the reproductive ability of both plants and animals. D Sexual dimorphismE None of the options is correct. B genes enhance survival of copies of themselves by directing organisms to assist others who share those genes.
Generalized by males reproductive success being limited by access to females and females reproductive success being limited by access to resources Resource distribution. We review mating systems and behaviors across ungulates and offer a new approach synthesizing how interacting factors may shape those mating systems. 63 The presence of altruistic behavior is most likely due to kin selection a theory maintaining A aggression between sexes promotes the survival of the fittest individuals.
Care required by young. However species in both syndrome groups. This empirical framework for.
Mating and reproductive systems affect the way that alleles are combined in individuals in a population. Mating systems are unique for each species and they are affected by the environmental condition and sexual selection. The evolution of mating systems is most likely.
Were being asked whether or not clutch size can affect the reproductive performance of the young. Pages 10 This preview shows page 6 - 8 out of 10 pages. The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by _____.
The idea that mating systems are the result of sexual conflict and resource distribution Sexual conflict Differential selection on males and females in order to maximize fitness. The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by A population density The evolution of mating systems is most likely School University of Illinois Urbana Champaign. Such information allows mating systems to be classified using data commonly available from ecological life history and behavioral analyses.
The possible mating systems span a continuum that ranges from 100 inbreeding to 100 outcrossing. 55 The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by A population size. B TerritorialityC Certainty of paternity.
Variability exists in mating systems among and within species of ungulates and likely is affected by predation risk availability of resources food and mates habitat structure and sociality. The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected by certainty of paternity. Collinsia is a genus of self-compatible mixed-mating species that differ markedly in floral morphological and developmental traits associated with mating system variation.
Mating systems are relevant only for organisms that undergo sexual reproduction. D B and C only E A B and C. 40 The evolution of mating systems is most likely affected byA Population density.
Population size care required by young and certainty of paternity. C certainty of paternity. Course Title BIOLOGY BIOB51.
And those eggs theyre gonna grew up and before adults with luck.
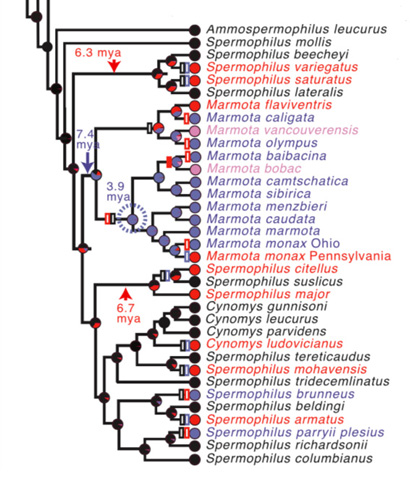
How Genetics And Social Games Drive Evolution Of Mating Systems In Mammals
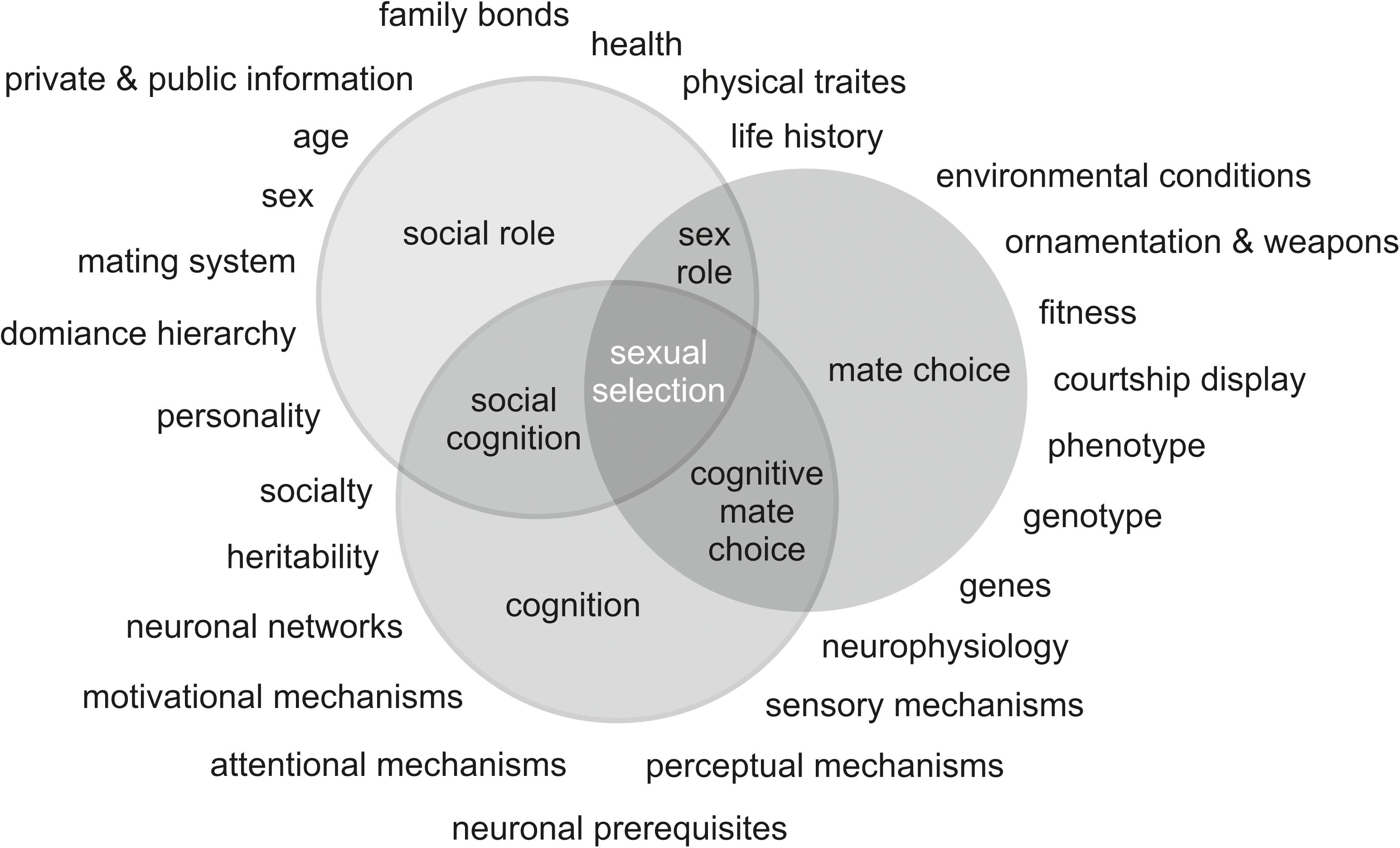
Frontiers Mate Choice Sex Roles And Sexual Cognition In Vertebrates Mate Choice Turns Cognition Or Cognition Turns Mate Choice Ecology And Evolution

Comments
Post a Comment